Esophageal Motility Disorders
Esophageal Motility Disorders
Normal swallowing causing pressure waves to move down the esophagus to propel food and water into the stomach. Esophageal motility disorders in contraction may include simultaneous contraction, loss of contraction, and abnormally high or low contractions. These disorders can cause difficulty swallowing with sticking sensation, heartburn, chest pain, and regurgitation.
Achalasia
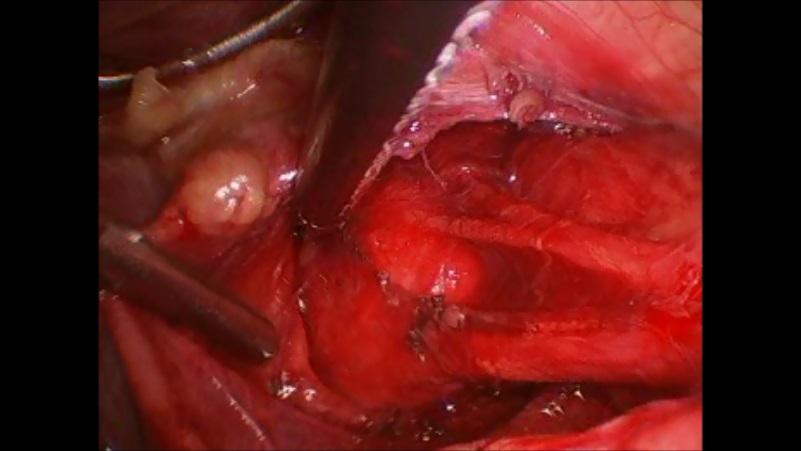
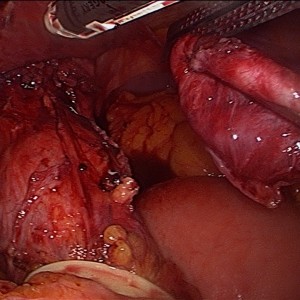
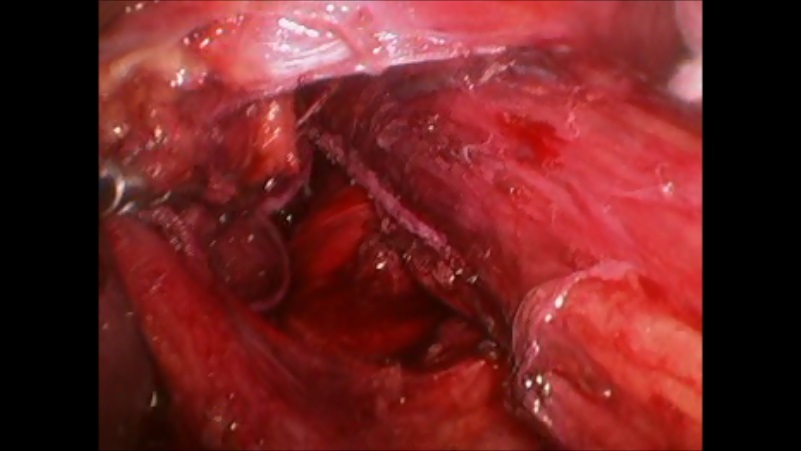
This is the most common esophageal motility disorder. Achalasia occurs when the lower esophageal sphincter (or the valve at the end of the esophagus) fails to relax. Often, this is seen with loss of contraction of the esophagus. Symptoms are usually of chest pain with swallowing and sticking, but it may also present as heartburn and regurgitation. Many people are inappropriately treated for GERD. A variant of achalasia is nutcracker esophagus which is often mistaken for cardiac pain. Medical treatment consists of medications to relax the muscles in the esophagus. These have significant side effects and are ineffective. Botox injection causes relaxation of the esophageal muscles and lasts for about 6 months. This often requires repeated injections and leads to scarring in the esophagus which makes definitive surgical treatment more complicated. This should be reserved for very old and sick patients that dont have a short life expectancy. Balloon dilation may also be performed to stretch or rupture the esophageal muscles. This has a significant perforation rate and should be used in select patients. Heller myotomy is the definitive treatment for achalasia with the highest lasting success rate. The hypertrophic muscles are divided laparoscopically under magnification. Studies show this can be done safely with low complications even in elderly patients with health problems. Diverticuli may be removed and anti-reflux procedure performed at the same time.